Siding Options for Modern Homes
Siding options for modern homes offer a plethora of choices, impacting not only aesthetics but also durability, energy efficiency, and cost. Understanding the diverse materials, their maintenance needs, and the potential impact on your home’s value is crucial in making an informed decision. From the classic charm of wood to the sleek lines of metal, this exploration will guide you through the many siding choices available for your modern home.
This comprehensive guide explores various siding materials, including vinyl, fiber cement, wood, and metal. We delve into their respective pros and cons, examining durability, maintenance, energy efficiency, and cost. Aesthetic considerations, design options, and installation procedures are also addressed to provide a holistic view of each siding type. A deeper understanding of these aspects will help you select the perfect siding for your modern home.
Introduction to Siding Options
Modern homes often prioritize aesthetics and durability, making siding selection a crucial aspect of the design process. Choosing the right siding material for a modern home involves careful consideration of both visual appeal and practical factors. The various options available offer diverse textures, colors, and maintenance requirements. Understanding these factors allows homeowners to make informed decisions that enhance the home’s value and longevity.
Modern siding choices extend beyond traditional materials, encompassing innovative options that provide contemporary appeal. The key aesthetic considerations for modern siding include the overall architectural style of the home, the desired color palette, and the texture or finish of the siding itself. These elements collectively contribute to the visual harmony and character of the structure.
Siding Materials Commonly Used in Modern Homes
Modern homes frequently utilize a range of siding materials, each with unique characteristics. These materials include vinyl, fiber cement, wood, and metal, each offering distinct advantages and disadvantages. Careful consideration of these differences is vital for selecting the optimal siding material for a specific project.
- Vinyl siding is a popular choice due to its affordability, low maintenance, and wide array of colors and styles. It’s relatively easy to install and comes in various textures to mimic natural materials. Vinyl’s resistance to rot, insects, and moisture makes it a suitable choice for diverse climates.
- Fiber cement siding is a composite material that blends cement, fibers, and other additives. It offers excellent durability, resistance to moisture, and a wide range of colors and textures. Its inherent strength and long lifespan are attractive features, often surpassing vinyl in terms of longevity.
- Wood siding provides a natural, warm aesthetic that complements many modern architectural styles. It offers a unique character and visual appeal. However, proper maintenance is essential to prevent decay and pest damage, requiring regular sealing and treatment.
- Metal siding, including steel and aluminum, presents a sleek and contemporary look. Its durability and resilience to harsh weather conditions make it a compelling choice. However, the initial cost can be higher than other options, and the appearance may not suit every architectural style.
Aesthetic Considerations for Modern Siding
Modern architectural styles often emphasize clean lines, geometric shapes, and a minimalist approach. The choice of siding should harmonize with these design elements. The color palette should complement the surrounding environment and the overall aesthetic of the home. Textures and finishes play a significant role in achieving the desired visual effect.
Styles and Textures Available for Modern Siding
Siding materials come in diverse styles and textures, allowing homeowners to personalize their homes. The options range from smooth and sleek finishes to textured imitations of natural materials. The choice of style and texture directly impacts the home’s aesthetic appeal.
- Smooth vinyl siding provides a contemporary and clean look, while wood-grain vinyl offers a more natural aesthetic.
- Fiber cement siding can mimic various natural materials, including wood, stone, and brick, offering diverse visual options.
- Wood siding’s natural texture can be enhanced with various finishes, from painted to stained options.
- Metal siding often comes in smooth or textured finishes, allowing for a sleek or rustic look, depending on the chosen texture.
Examples of Siding Materials Used in Modern Home Designs
Numerous modern homes showcase the use of various siding materials. For example, sleek vinyl siding is frequently seen in contemporary homes with a minimalist aesthetic. Fiber cement siding’s versatility allows it to be integrated into modern homes with a variety of architectural styles. Wooden siding complements modern homes with a touch of warmth and character. Metal siding, often seen in industrial or modern designs, offers a unique and bold aesthetic.
Comparison of Siding Types
The following table compares the pros and cons of different siding types for modern homes.
| Siding Type | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Vinyl | Affordable, low maintenance, wide range of colors and styles, easy installation, resistant to rot, insects, and moisture | It can be less durable than other options, may not have the same visual appeal as other materials, and can be susceptible to impact damage. |
| Fiber Cement | Durable, resistant to moisture, a wide range of colors and textures, long lifespan, high resistance to rot, insects, and impact damage | It has a higher initial cost compared to vinyl, may not be as aesthetically versatile as vinyl, and can be heavier than other materials. |
| Wood | Natural, warm aesthetic, unique character, can be customized with various finishes. | Requires regular maintenance (sealing, treatment), is susceptible to decay and pest damage, and may not be as durable as other options |
| Metal | Durable, resilient to harsh weather conditions, sleek and contemporary look, long lifespan, low maintenance | Higher initial cost, may not suit all architectural styles, potential for noise issues with some types |
Durability and Maintenance: Siding Options For Modern Homes

Choosing the right siding for your modern home involves careful consideration of its long-term performance. Factors like climate, maintenance needs, and resistance to damage play crucial roles in the overall lifespan and value of your property. Understanding these aspects ensures that you make an informed decision that aligns with your lifestyle and the expected longevity of your home’s exterior.
Long-Term Durability in Various Climates
Different siding materials exhibit varying degrees of durability depending on the climate. Vinyl siding, for instance, performs well in humid regions due to its resistance to moisture damage. However, in extremely cold climates, it might be susceptible to cracking or warping. Fiber cement siding offers excellent durability in both humid and cold climates, resisting rot, mold, and warping. Wood siding, while attractive, requires more maintenance and is less durable in areas with high humidity or extreme temperatures. Metal siding, often made from aluminum or steel, stands up well in most climates, offering excellent resistance to weather and pests.
Maintenance Requirements for Different Siding Types
Regular maintenance is essential to preserve the aesthetic appeal and structural integrity of any siding material. Vinyl siding requires minimal upkeep, primarily cleaning with soap and water. Fiber cement siding needs periodic cleaning and occasional inspections for damage. Wood siding necessitates regular cleaning, sealing, and painting to prevent rot and insect infestation. Metal siding generally demands the least maintenance, needing only occasional cleaning to remove dirt and debris.
Resistance to Weather Damage and Pests
Siding materials differ significantly in their resistance to weather damage and pest infestations. Vinyl siding is resistant to rot and insect damage but may be vulnerable to high winds or hail. Fiber cement siding excels in withstanding various weather conditions and is generally resistant to insects. Wood siding is susceptible to rot, insects, and water damage if not properly maintained. Metal siding stands up well against wind, rain, and hail and provides good protection against pests.
Lifespan of Different Siding Materials
The lifespan of siding materials varies depending on factors such as material quality, installation, and climate conditions. Vinyl siding typically lasts 50-75 years with proper maintenance. Fiber cement siding has a projected lifespan of 50 years or more, offering substantial longevity. Wood siding, without regular upkeep, can last 15-25 years. Metal siding, particularly when properly installed, can endure for 50 years or more.
Average Maintenance Schedule
| Siding Type | Maintenance Schedule |
|---|---|
| Vinyl | Annual cleaning with soap and water, occasional inspection for damage. Check for warping or cracking, especially in cold climates. |
| Fiber Cement | Annual cleaning with mild detergent and water, inspect for damage every 2-3 years, especially in high-moisture areas. |
| Wood | Annual cleaning, sealing, and painting. Inspect for rot and insect damage, and address any problems promptly. Consider applying a sealant or stain every 2-3 years. |
| Metal | Occasional cleaning with mild detergent and water. Inspect for dents or damage from weather or impacts. |
Energy Efficiency and Insulation
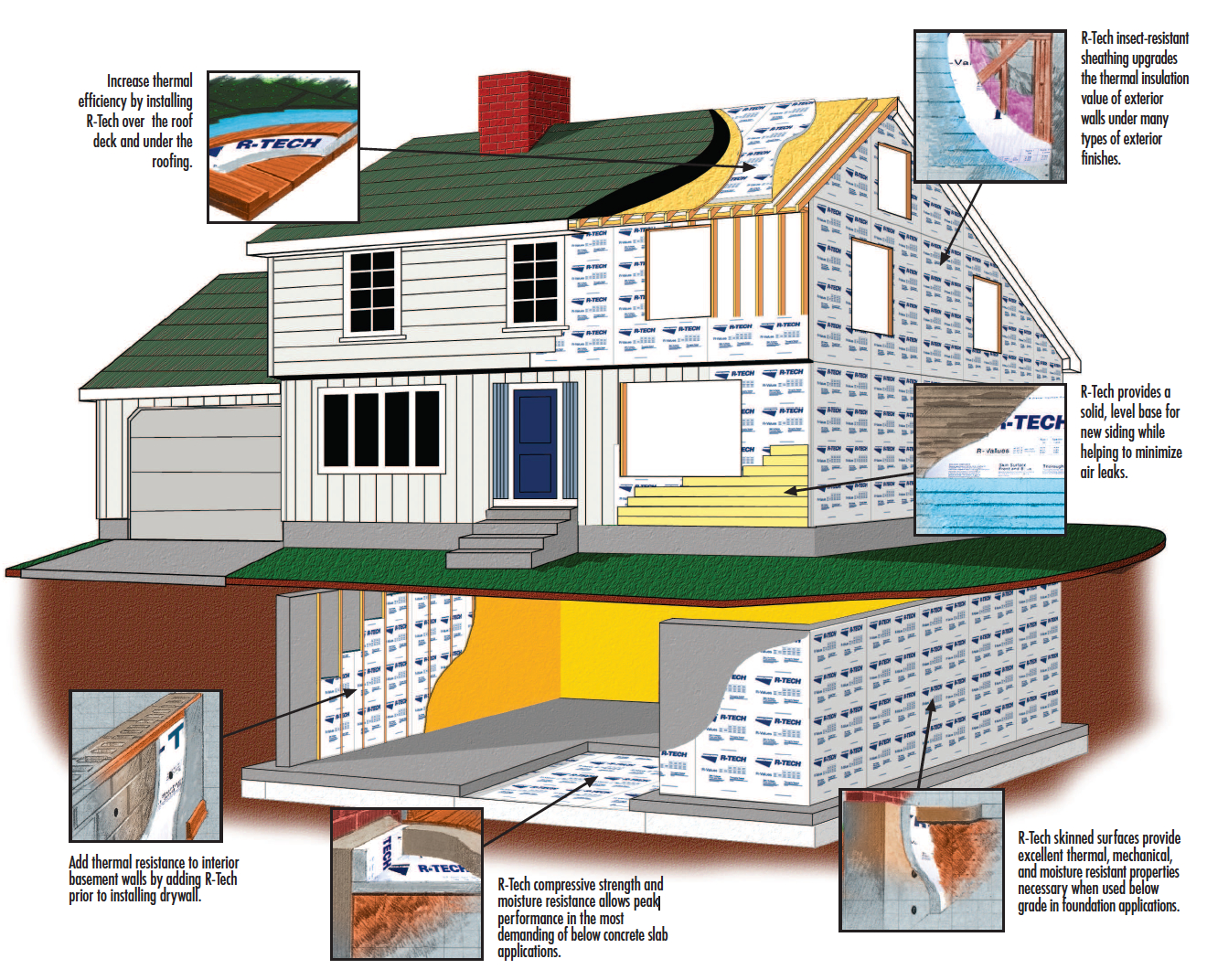
Choosing siding for your modern home goes beyond aesthetics; it significantly impacts energy efficiency and comfort. Different materials and their associated insulation strategies play a crucial role in regulating indoor temperatures, minimizing energy consumption, and ultimately lowering your energy bills. Understanding these relationships is key to making informed decisions.
Proper siding selection, coupled with strategic insulation, creates a thermal envelope that efficiently manages heat gain and loss, optimizing indoor temperatures year-round. This approach translates to substantial savings on energy bills and a more comfortable living environment.
Impact of Siding Materials on Energy Efficiency
Different siding materials have varying thermal properties, influencing how effectively they insulate a home. Materials with higher thermal resistance (lower thermal conductivity) perform better at preventing heat transfer. For instance, materials like fiber cement and metal siding, when properly installed and insulated, can contribute to a more energy-efficient home compared to less thermally resistant options. Properly installed siding, in combination with adequate insulation, is critical to reducing heat loss and gain.
Role of Insulation in Siding Systems
Insulation within a siding system is critical for maintaining a comfortable indoor temperature and minimizing energy loss. The insulation acts as a barrier, reducing the amount of heat that escapes in winter and enters in summer. The type and thickness of insulation significantly impact a home’s energy efficiency. Proper installation methods are essential to ensure the insulation’s effectiveness, preventing air gaps or inadequate coverage.
Impact of Siding on Energy Bills and Home Comfort
The right siding and insulation combination can noticeably reduce energy bills. By preventing heat transfer, energy-efficient siding and insulation systems maintain a more consistent indoor temperature. This results in lower heating and cooling demands, translating directly into savings on utility bills. Improved home comfort is another key benefit. Homes with well-insulated siding and proper insulation experience fewer temperature fluctuations, leading to a more stable and comfortable living environment.
Various Insulation Options for Different Siding Types
The choice of insulation often depends on the type of siding used. Different materials react differently to insulation types. For instance, vinyl siding can effectively be paired with various insulation options such as foam board or spray foam, while metal siding might benefit from the use of rigid foam board insulation. Wood siding may also benefit from various insulation options, including batts, blankets, or cellulose. The correct selection of insulation is critical for maximizing energy efficiency and minimizing thermal bridging.
Table Demonstrating R-Values of Siding and Insulation Combinations
| Siding Type | Insulation Options | R-Value (estimated) |
|---|---|---|
| Vinyl | Foam board insulation (2 inches), air barrier | 3.5-5.0 |
| Fiber Cement | Foam board insulation (2 inches), air barrier | 4.0-5.5 |
| Wood | Rigid foam board insulation (2 inches), air barrier | 4.5-6.0 |
| Metal | Rigid foam board insulation (2 inches), air barrier | 4.0-6.0 |
Note: R-values are estimates and can vary based on specific product types, installation techniques, and climate conditions. Consult with a qualified professional for personalized recommendations.
Cost Considerations
Choosing the right siding for your modern home involves more than just aesthetics and performance; a crucial factor is the cost. Understanding the initial material costs, installation expenses, and long-term ownership costs is essential for making an informed decision. A thorough assessment of these elements can help homeowners budget effectively and avoid potential financial surprises.
Initial Material Costs
Different siding materials have varying price points. Vinyl siding, a popular and affordable option, typically has a lower initial cost compared to fiber cement or wood siding. Fiber cement, while offering superior durability, often comes with a higher upfront price tag. Metal siding, with its diverse styles and finishes, can range in cost depending on the type of metal used and the specific design choices. Wood siding, while aesthetically pleasing, usually carries a higher initial cost compared to vinyl or metal, reflecting the material’s inherent value and the craftsmanship involved in its installation.
Installation Costs
Installation costs for siding vary significantly depending on the complexity of the project, the size of the home, and the specific siding material. Vinyl siding, with its relatively straightforward installation process, generally has lower installation costs than fiber cement or wood siding. The labor involved in installing complex or intricate designs for any siding type can increase the overall installation cost. Factors such as the condition of the existing structure, the presence of any necessary repairs, and the need for specialized equipment can also impact the cost of installation.
Long-Term Cost of Ownership
The long-term cost of ownership considers not only the initial investment but also the ongoing maintenance and potential repairs over time. While vinyl siding might have a lower initial cost, its lower maintenance requirements often translate to a lower long-term cost of ownership. Fiber cement, with its superior durability, could have a higher initial price, but its resistance to damage and extended lifespan can make it a more economical choice in the long run. Wood siding, despite its beauty, demands more frequent maintenance, which can lead to higher long-term costs due to the need for repainting, sealing, and potential repairs. Metal siding, with its excellent longevity and durability, can offer a competitive long-term cost of ownership, depending on the specific metal type and the longevity of the product.
Factors Influencing Final Cost
Numerous factors influence the final cost of a siding project. The size and complexity of the home, the extent of any necessary repairs or renovations, and the labor costs in your area all play a role. Local building codes and permitting requirements can also add to the overall project cost. The choice of siding material and the desired level of customization also directly impact the final cost. Additional considerations include the need for specialized equipment or skilled labor for certain siding types.
Estimated Costs for Different Siding Types
| Siding Type | Initial Cost | Installation Cost | Total Estimated Cost |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vinyl | $5-$15 per square foot | $5-$15 per square foot | $10-$30 per square foot |
| Fiber Cement | $10-$25 per square foot | $8-$18 per square foot | $18-$43 per square foot |
| Wood | $10-$30 per square foot | $10-$25 per square foot | $20-$55 per square foot |
| Metal | $12-$30 per square foot | $8-$20 per square foot | $20-$50 per square foot |
Note: These are estimated costs and can vary significantly based on location, specific material choices, and project scope. Professional consultation with contractors is recommended for accurate project-specific pricing.
Aesthetics and Design Options

Choosing siding for a modern home is more than just practicality; it’s a significant design element that shapes the home’s overall aesthetic and architectural appeal. The right siding can complement the home’s design, creating a cohesive and visually striking appearance. This section explores the diverse aesthetic possibilities offered by various siding materials, highlighting their visual impact and suitability for different modern architectural styles.
Different siding materials offer a spectrum of aesthetic possibilities, ranging from the clean lines of wood to the sleek sophistication of metal. The color palettes, finishes, and textures available for each material contribute to the overall visual appeal and can dramatically influence the home’s personality.
Siding Material Aesthetics
Various siding materials provide distinct aesthetic characteristics. Wood siding, for instance, offers a warm, natural look, while vinyl siding provides a range of colors and styles that can mimic other materials. Fiber cement siding offers a more durable and low-maintenance option with a refined aesthetic. Metal siding provides a modern, contemporary appeal, particularly suited to minimalist designs. Each material presents unique design opportunities that can be tailored to suit specific architectural preferences.
Color Options and Finishes
The availability of colors and finishes significantly impacts the visual appeal of a home. Wood siding, for example, can be stained or painted in various shades, from warm neutrals to bold contemporary colors. Vinyl siding offers a wide spectrum of colors, allowing homeowners to select shades that complement their surroundings and architectural style. Fiber cement siding typically comes in a range of neutral colors, though some manufacturers offer more contemporary options. Metal siding often features a sleek, metallic finish, but some options come with painted or textured surfaces for greater design flexibility.
Enhancing Architectural Style, Siding options for modern homes
The choice of siding directly impacts the architectural style of a modern home. A modern home with clean lines might benefit from sleek metal si smooth vinyl siding. A home with a more traditional feel might opt for natural wood siding, but even this choice can be modified to complement the modern aesthetic through careful color and finish selection. Siding materials can visually emphasize the home’s design elements, such as gables, eaves, or architectural details.
Visual Appeal Comparison
| Siding Material | Visual Appeal | Suitability for Modern Homes |
|---|---|---|
| Wood | Warm, natural, inviting | Excellent for homes with a modern farmhouse or Craftsman aesthetic |
| Vinyl | Versatile, wide color range, low maintenance | Suitable for most modern styles, easily adaptable to different colors and designs |
| Fiber Cement | Durable, low-maintenance, refined look | Excellent choice for homes with modern or contemporary designs |
| Metal | Sleek, contemporary, modern | Ideal for minimalist, modern, and contemporary homes |
Color Palettes and Design Elements
The right color palette and design elements can elevate the visual appeal of a modern home.
- Modern Neutrals: A palette of soft grays, whites, and creams creates a clean, sophisticated look that complements various modern architectural styles. This palette works well with most siding materials.
- Bold Accents: Incorporating bold colors or contrasting accents can add visual interest and personality to a modern home. Deep blues, rich greens, or vibrant reds can be used strategically to highlight architectural features or create focal points.
- Warm Tones: A palette of warm beiges, browns, and creams can create a cozy and inviting atmosphere, particularly suitable for homes with large windows and natural light. This approach is well-suited to wood siding.
- Exterior Design Elements: Consider the use of shutters, trim, and other exterior design elements to further enhance the visual appeal. These elements can complement the chosen siding material and color scheme.
Image Descriptions
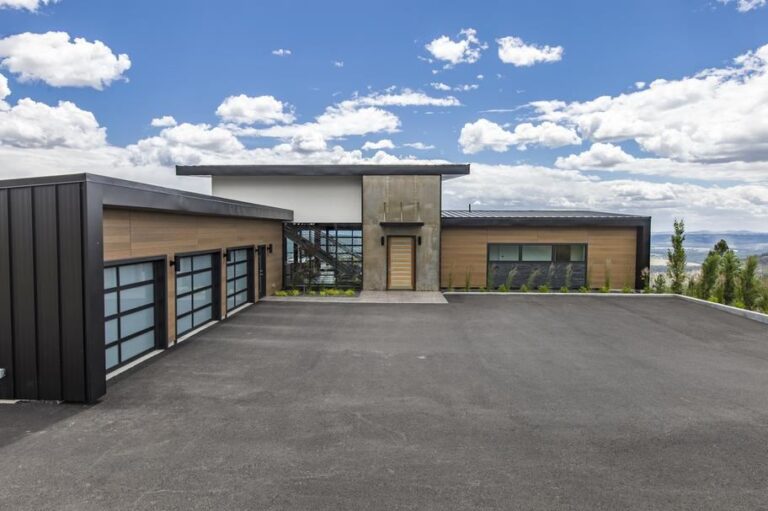
Image 1: A modern home featuring gray vinyl siding. The siding has a smooth, contemporary finish. The house has a clean, minimalist design, with large windows and a flat roof. The overall effect is one of sleekness and sophistication.
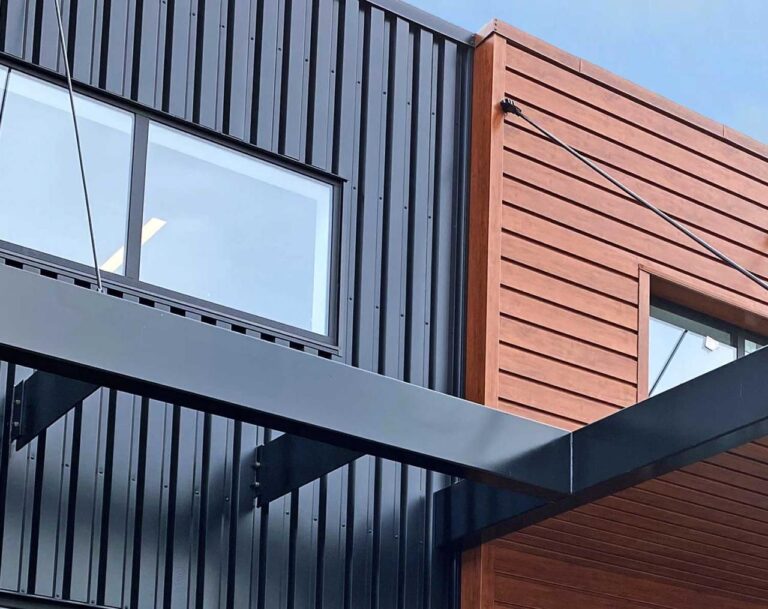
Image 2: A modern home with dark-gray fiber cement siding. The siding features subtle horizontal lines that create a sense of depth and dimension. The house has a modern, geometric design with large windows and an angular roof. The color and material provide a strong, modern aesthetic.
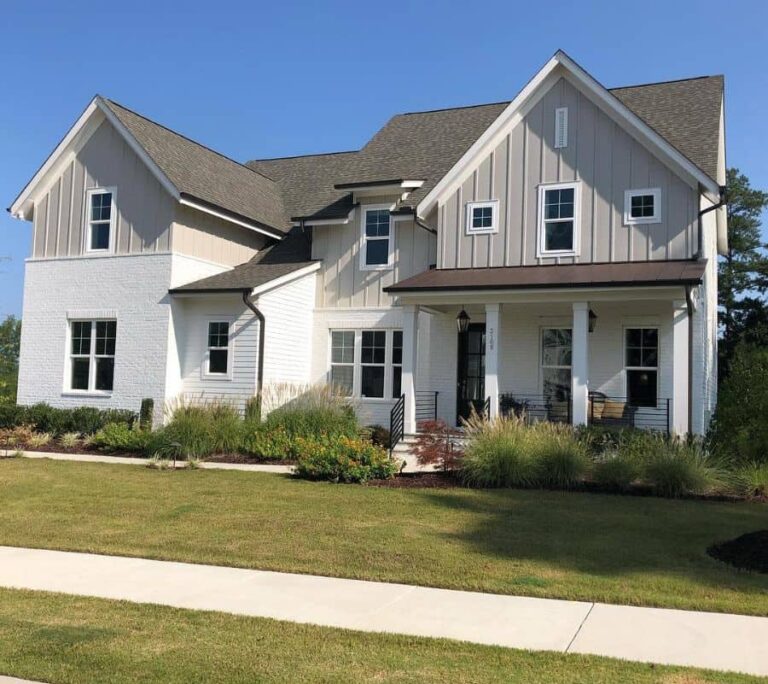
Image 3: A modern home with light beige wood siding. The siding has a natural wood grain texture, giving the home a warm and inviting feel. The house has a modern design with a slightly more traditional feel, featuring a pitched roof and smaller windows. The combination of the siding material and color gives the home a sense of rustic modernism.
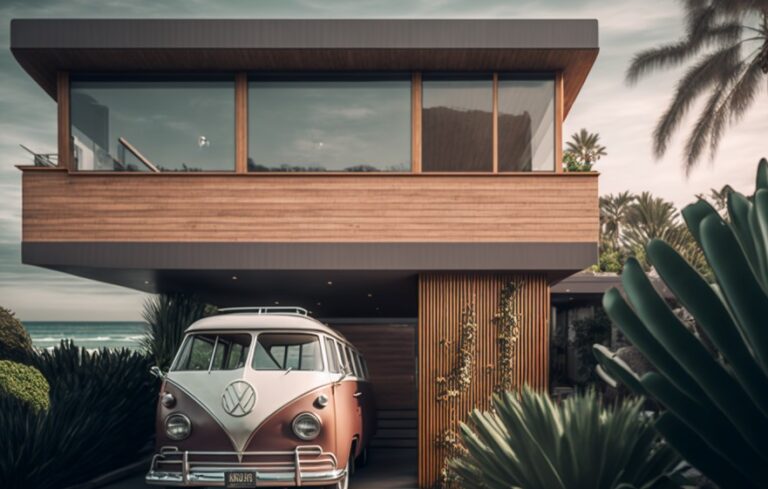
Image 4: A modern home with sleek black metal siding. The siding has a smooth, metallic finish. The house features a minimalist design with large windows and a flat roof. The effect is modern, sleek, and contemporary.
Installation and Maintenance Considerations
Choosing the right siding for your modern home involves more than just aesthetics; proper installation and ongoing maintenance are crucial for longevity and performance. These factors significantly impact the overall value and enjoyment of your home. Careful consideration of the installation process and subsequent maintenance routines can prevent costly repairs and ensure your siding remains a beautiful and functional element of your home for years to come.
Installation Processes for Different Siding Materials
Different siding materials necessitate distinct installation approaches. Understanding these variations is key to achieving a successful and durable installation. The steps and considerations involved in installing vinyl, fiber cement, wood, and metal siding differ significantly, impacting the overall project timeline and labor costs.
| Siding Type | Installation Steps |
|---|---|
| Vinyl | Vinyl siding installation typically involves attaching the panels to the existing framing using specialized clips and fasteners. Careful measurement and precise application of the adhesive are critical for a watertight and secure installation. Proper ventilation and spacing between panels are important to prevent moisture buildup. Seams and joints require meticulous attention to detail to avoid leaks and ensure a professional finish. |
| Fiber Cement | Fiber cement siding, often chosen for its durability, typically involves attaching the panels to the existing framing using screws and specialized clips. Properly securing the panels to the supporting structure is essential for long-term structural integrity. Adhering to manufacturer recommendations for spacing and ventilation is paramount for preventing water damage. A meticulous installation ensures a strong and weather-resistant barrier. |
| Wood | Wood siding, a classic choice for its natural beauty, requires careful preparation of the framing and the wood panels. Thorough priming and sealing are essential to protect the wood from moisture damage and rot. Fasteners, such as nails or screws, should be appropriately sized and spaced to avoid damage to the wood and ensure structural integrity. Proper ventilation is critical to preventing moisture build-up and decay. |
| Metal | Metal siding installation, often favored for its low-maintenance nature, usually involves attaching the panels to the existing framing using specialized clips and fasteners. Precise measurements and secure attachment are vital to ensure the panels’ alignment and prevent damage. Proper consideration of expansion and contraction is essential for maintaining the integrity of the siding over time. Ensuring proper drainage is crucial to avoid water accumulation. |
Steps Involved in Proper Siding Maintenance
Regular maintenance is crucial for preserving the beauty and performance of your siding. Preventive measures can extend the lifespan of your siding, reducing the need for costly repairs. Understanding the specific maintenance needs of each material is key to maintaining its integrity.
- Regular Inspections: Visual inspections should be performed periodically to identify any signs of damage, such as cracks, gaps, or loose panels. Early detection and prompt repairs can prevent further damage and costly replacements.
- Cleaning: Regular cleaning can remove dirt, debris, and mold that may accumulate on the siding. Use appropriate cleaning solutions and techniques to avoid damaging the siding material. A thorough cleaning helps maintain the siding’s appearance and prevents the growth of mildew and algae.
- Sealant Maintenance: Inspect and reapply sealant around joints, seams, and corners as needed to prevent water intrusion and maintain the siding’s weather-resistant properties. Regular sealing ensures a watertight barrier and protects against moisture damage.
- Addressing Damage Promptly: If any damage, such as cracks, dents, or loose panels, is discovered, it should be addressed promptly to prevent further deterioration. Addressing issues quickly minimizes the extent of the damage and helps maintain the siding’s integrity.
Potential Issues During Installation and Maintenance
Various issues can arise during installation and maintenance, from simple errors to more serious structural problems. Careful attention to detail and adherence to manufacturer guidelines are crucial to mitigate these potential problems.
- Improper Installation: Incorrect installation techniques, such as inadequate fastening or improper spacing, can lead to leaks, structural issues, and premature siding failure. Proper installation procedures are essential for achieving a durable and long-lasting result.
- Water Damage: Improper drainage or inadequate sealing can lead to water damage, resulting in rot, mildew, and structural damage. Promptly addressing water issues is critical for preventing extensive damage.
- Pest Infestation: Wood siding is particularly susceptible to pest infestations, which can lead to significant damage. Regular inspections and pest control measures can prevent infestations and protect the siding from decay.
- Material Degradation: Exposure to harsh weather conditions, UV radiation, and other environmental factors can degrade the material over time. Choosing materials that are resistant to these factors and using proper maintenance practices are vital for extending the lifespan of your siding.
Comparing Ease of Installation
The ease of installation varies considerably between different siding materials. Factors such as the complexity of the installation process, required tools, and expertise influence the overall ease of installation. Professional installation is often recommended for complex projects or for achieving optimal results.
- Vinyl: Vinyl siding is generally considered relatively easy to install, requiring fewer specialized tools and allowing for greater flexibility in installation techniques.
- Fiber Cement: Fiber cement installation is slightly more complex than vinyl, requiring specialized tools and potentially more time for installation.
- Wood: Wood siding installation can be more complex and time-consuming due to the need for precise measurements and careful handling of the material.
- Metal: Metal siding installation is typically more complex, often requiring specialized tools and expertise to ensure proper alignment and secure attachment.
Last Word

Source: pinimg.com
In conclusion, selecting the right siding for your modern home is a multifaceted decision. Consideration of aesthetics, durability, maintenance, energy efficiency, and cost are essential factors. This guide has presented a thorough overview of siding options, allowing you to make an informed choice that complements your home’s architectural style while meeting your long-term needs. Ultimately, the ideal siding selection will enhance your home’s beauty, value, and comfort for years to come.





